
In today’s rapidly evolving workplace, electric furniture repair represents a critical intersection of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology. From smart desks and powered recliners to integrated office systems, the complexity of electronic furniture components demands specialized knowledge and systematic repair approaches. Industry data shows a 47% increase in electronic furniture installations across commercial spaces since 2019, making efficient repair services more essential than ever.
For facility managers and business owners, mastering electric furniture repair isn’t just about fixing broken components—it’s about maintaining productivity, ensuring workplace safety, and protecting significant investments. Modern electric furniture systems, often costing upwards of $10,000 per workstation, require precise diagnostic protocols and professional repair solutions to maintain their functionality and extend their lifespan.
The convergence of supply chain optimization and furniture repair services creates unique opportunities for businesses to streamline operations, reduce downtime, and maximize resource utilization. Whether managing a corporate office space, healthcare facility, or educational institution, understanding the intricacies of electric furniture repair within the supply chain context has become a fundamental aspect of operational excellence.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of electric furniture repair, from diagnostic procedures and inventory management to cost-effective maintenance strategies and future trends in smart furniture technology.
Today’s electric furniture features sophisticated components that make our seating and sleeping experience more comfortable and convenient. As modern technology in furniture repair continues to evolve, understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance and repair.
Common electronic elements include linear actuators, which control reclining mechanisms and adjustable headrests in powered sofas and chairs. Power transformers and control boxes serve as the central nervous system, converting household current into usable power while managing various functions. Most pieces feature membrane switches or push-button controls, allowing users to adjust positions easily.
USB charging ports have become standard in contemporary furniture, requiring specialized wiring harnesses and power delivery systems. Motion sensors and massage motors are frequently found in high-end recliners and beds, while LED lighting systems are increasingly integrated into entertainment units and headboards.
Heat and cooling systems, particularly in luxury massage chairs, utilize thermoelectric components and specialized control modules. Battery backup systems are also common, ensuring functionality during power outages and providing surge protection for sensitive electronics.
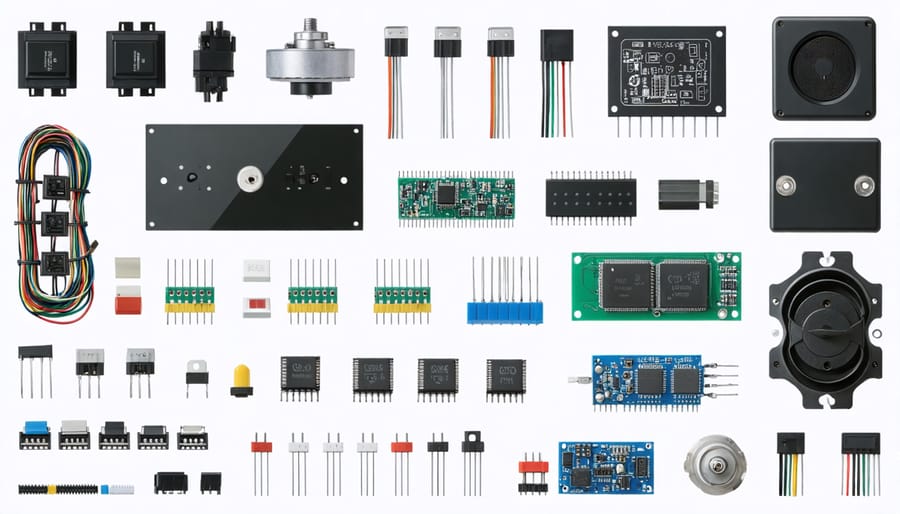
Managing electronic components for furniture repair requires careful attention to both sourcing and storage practices. Reliable suppliers are essential, as counterfeit or substandard electronic parts can compromise repair quality and safety. We recommend establishing relationships with multiple certified distributors to ensure consistent availability of critical components like circuit boards, motors, and control panels.
Temperature-controlled storage is crucial for electronic parts, with humidity levels maintained between 30-50% to prevent corrosion and static damage. Implementing a first-in-first-out (FIFO) inventory system helps track component age and reduces waste from expired parts.
Common challenges include minimum order quantities and lead times for specialized components. To address this, maintain a strategic inventory of frequently-needed parts while developing relationships with local suppliers for emergency purchases. Regular market analysis helps anticipate price fluctuations and potential shortages.
For quality assurance, document all component specifications and establish testing procedures before installation. This includes verifying voltage requirements, compatibility with existing systems, and adherence to safety standards. Consider implementing a barcode system for accurate tracking and streamlined reordering processes.
Managing electronic components for furniture repair requires a sophisticated inventory system that balances stock levels with repair demands. Modern repair shops utilize specialized software platforms that track both common components like power supplies, motors, and control boards, as well as rare or discontinued parts specific to certain furniture brands.
These systems typically feature barcode scanning capabilities, allowing technicians to quickly locate and track parts usage. Real-time inventory updates help prevent stockouts of critical components while maintaining optimal inventory levels. Smart reordering systems automatically generate purchase orders when stock reaches predetermined minimum levels, ensuring continuous service availability.
Component lifecycle tracking is another crucial feature, helping shops monitor the age and condition of stored parts. This is particularly important for electronic components that may have shelf-life limitations or require specific storage conditions to maintain functionality.
Cloud-based inventory systems enable multi-location businesses to share resources efficiently. When one location needs a specialized component, they can quickly check availability across the network. This interconnectivity reduces overall inventory costs and improves repair turnaround times.
For warranty and quality control purposes, these systems maintain detailed records of part origins, installation dates, and repair histories. This documentation helps shops maintain compliance with manufacturer specifications while providing transparent service records to customers.
Many modern inventory systems also integrate with accounting software, streamlining cost tracking and helping businesses maintain profitable pricing structures for their repair services.
Quality control in electric furniture repair demands a systematic approach to ensure safety and functionality. Our comprehensive testing protocol begins with a thorough visual inspection of all electrical components, followed by voltage testing using calibrated multimeters and specialized diagnostic equipment.
Each repair undergoes a three-phase verification process. First, technicians conduct resistance measurements to verify circuit integrity and identify potential short circuits. Second, they perform load testing to ensure components can handle their rated power requirements without overheating. Finally, they subject the repaired item to a 24-hour operational test under normal usage conditions.
Documentation plays a crucial role in our quality control system. Every repair receives a detailed checklist covering safety compliance, performance standards, and cosmetic finish. Technicians must photograph key repair stages and record all measurements in our digital tracking system for future reference.
For motorized furniture like recliners and adjustable beds, we implement additional motion testing protocols. This includes checking for smooth operation, testing emergency backup systems, and verifying all limit switches function correctly. We also measure noise levels to ensure they fall within acceptable ranges.
Our final quality assurance step involves having a senior technician independently verify all repairs before client delivery. This dual-verification system has helped us maintain a 99.8% first-time fix rate and consistently exceed industry safety standards.
Becoming a qualified electric furniture repair technician requires a comprehensive blend of education, practical experience, and ongoing professional development. At minimum, technicians should possess a high school diploma or equivalent, followed by specialized training in electrical systems and furniture mechanics. Many successful technicians complete vocational programs or apprenticeships that focus on developing specialized repair skills for various furniture types.
Essential certifications include basic electrical safety credentials and manufacturer-specific training for popular furniture brands. Most employers require technicians to obtain certification from recognized industry bodies such as the Electrical Apparatus Service Association (EASA) or similar organizations. Additionally, technicians should maintain current knowledge of local electrical codes and safety regulations.
Key skills that technicians must develop include:
– Electrical troubleshooting and diagnostics
– Circuit board repair and replacement
– Motor and actuator maintenance
– Upholstery basics for accessing internal components
– Customer service and communication
– Digital diagnostic tool operation
Continuing education is crucial as furniture technology evolves. Successful technicians regularly attend workshops, manufacturer training sessions, and industry conferences to stay current with new repair techniques and emerging furniture technologies. Many companies also require periodic safety certifications renewal and skills assessment to ensure service quality and compliance with industry standards.

Effective parts procurement is crucial to maintaining a successful electric furniture repair operation while helping to optimize repair costs. Start by establishing relationships with multiple reliable suppliers to ensure consistent availability and competitive pricing. Consider both original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and authorized aftermarket parts distributors to maintain quality while managing expenses.
Implement a just-in-time inventory system for commonly needed components like motors, control boards, and power supplies. This approach reduces storage costs while ensuring parts availability for routine repairs. For specialty items, develop partnerships with local suppliers who can provide quick turnaround times on orders.
Create a database of compatible parts across different furniture brands and models. This knowledge allows for strategic bulk purchasing of universal components that work across multiple repair jobs. Consider joining industry buying groups or cooperatives to access better pricing through collective purchasing power.
Digital inventory management systems can help track parts usage patterns and automatically generate purchase orders when stock reaches predetermined levels. This prevents both overstock situations and repair delays due to parts shortages.
For vintage or discontinued furniture, develop relationships with salvage yards and restoration specialists who can provide hard-to-find components. Additionally, consider 3D printing capabilities for custom parts when original replacements are unavailable or cost-prohibitive.
Setting competitive repair rates for electric furniture requires a balanced approach that considers both market demands and operational costs. Most successful repair services adopt one of three primary pricing models: flat-rate pricing, hourly rates, or component-based pricing.
Flat-rate pricing offers customers peace of mind with predetermined costs for common repairs. For example, a standard motor replacement might be priced at $150-200, regardless of the time invested. This model works well for routine repairs where the scope of work is predictable.
Hourly rates typically range from $75-150 per hour, depending on your market and expertise level. This model is particularly suitable for complex repairs where the extent of damage isn’t immediately apparent. Many professionals combine this with a minimum service call fee of $50-75 to cover initial diagnostics and travel time.
Component-based pricing factors in both parts and labor, with a markup on replacement components (usually 30-50%) plus a base labor charge. This approach provides transparency and helps customers understand the value they’re receiving.
For commercial clients, consider offering service contracts with preferential rates. Monthly or annual maintenance agreements can provide steady income while offering clients discounted rates on emergency repairs.
Remember to regularly review and adjust your pricing structure based on:
– Local market conditions
– Competition analysis
– Operating costs
– Skill level required
– Parts availability
– Service urgency
This ensures your business remains profitable while delivering value to customers.
The landscape of electric furniture repair is rapidly evolving with groundbreaking technological advancements. As smart furniture technology trends continue to reshape the industry, repair technicians are adapting to meet new challenges and opportunities.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) integration are becoming increasingly prevalent in modern furniture diagnostics. Smart sensors embedded in electric furniture can now detect potential issues before they become major problems, allowing for predictive maintenance rather than reactive repairs. This transformation is particularly beneficial for commercial property managers and facility maintenance teams who can schedule repairs during off-peak hours.
3D printing technology is revolutionizing parts replacement, enabling technicians to create custom components on-demand. This advancement significantly reduces waiting times for replacement parts and ensures perfect fits for obsolete or discontinued furniture pieces. Additionally, augmented reality (AR) tools are empowering technicians to visualize internal components and wiring systems without physical disassembly, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Remote diagnostics and repair capabilities are gaining traction, allowing technicians to troubleshoot basic issues through video consultations and smart device connections. This trend not only reduces service costs but also improves response times for simple repairs. For complex issues, technicians can arrive better prepared with the right tools and replacement parts.
Sustainability is driving innovation in repair methods, with a growing focus on eco-friendly solutions and recyclable components. Modern electric furniture is being designed with modular components that are easier to repair and replace, reducing waste and extending furniture lifespan.
To stay competitive, repair services are investing in training programs that combine traditional repair skills with digital expertise. This hybrid approach ensures technicians can handle both legacy furniture systems and cutting-edge smart furniture, providing comprehensive service solutions for all clients.
In today’s rapidly evolving marketplace, efficient management of electric furniture repair operations has become crucial for business success. By implementing the strategies and best practices discussed throughout this article, supply chain managers can significantly improve their repair service operations while reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Remember to prioritize preventive maintenance programs, which can reduce emergency repairs by up to 40%. Establish strong relationships with reliable parts suppliers and maintain optimal inventory levels to ensure quick turnaround times. The implementation of digital tracking systems and automated inventory management solutions has proven to reduce operational costs by an average of 25% while improving service delivery times.
Training and certification programs for repair technicians should remain a top priority, as skilled professionals directly impact service quality and customer retention rates. Consider implementing a hybrid service model that combines in-house expertise with strategic outsourcing partnerships for specialized repairs.
Looking ahead, stay informed about emerging technologies and sustainable practices in furniture repair. The integration of IoT sensors and predictive maintenance capabilities will continue to reshape the industry, offering new opportunities for efficiency and service improvement.
Take action today by assessing your current repair operations, identifying areas for improvement, and developing a structured implementation plan. Remember that successful electric furniture repair management is an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation and adaptation to changing market demands and technological advancements.